How To Diagnose And Fix Problems On Samsung Phones Using Samsung Members App
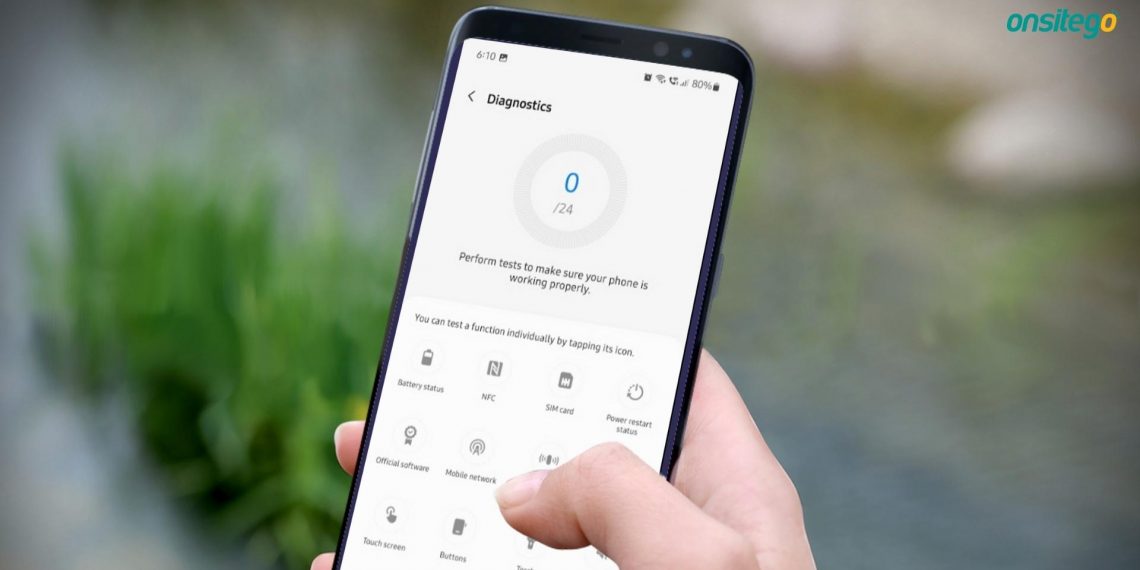
In today’s cut-throat smartphone market, Samsung has carved out its name for obvious reasons. To users, Samsung isn’t just another smartphone company. It offers great software and reliability and arguably offers the best after-sales service worldwide. However, smartphones aren’t perfect, and there might be instances when you might face troubles with one thing or the other with no one around to help you with your problem.
This is where the Samsung Members app comes in. If you have a Samsung smartphone, you can use diagnostic tips and tutorials to find out major issues. And then you can have a better idea of how to solve the problem. In this post, we will take a look at how you can use the Samsung Members app to diagnose and fix the most common issues on Samsung smartphones.
What Is the Samsung Members Application? What Can It Do?
Samsung Members is an official Android app from Samsung, and you can install it from Galaxy Store or Google Play Store. It can help you detect potential issues with your phone by conducting diagnostic tests and offering valuable troubleshooting tips.
Official announcements, insider news, knowledge base, and know-how from professionals are also available on the app. There’s also a separate comprehensive area for FAQs, which contains answers to commonly asked issues so Samsung smartphone users can access them at any time, anywhere.
Here’s an example of a potential use case: If your fingerprint sensor is acting up or your phone isn’t charging when plugged into a power outlet, the app will let you know what’s the exact issue could be.
Samsung Members App: How To Use It To Diagnose Problems On Your Galaxy Smartphone
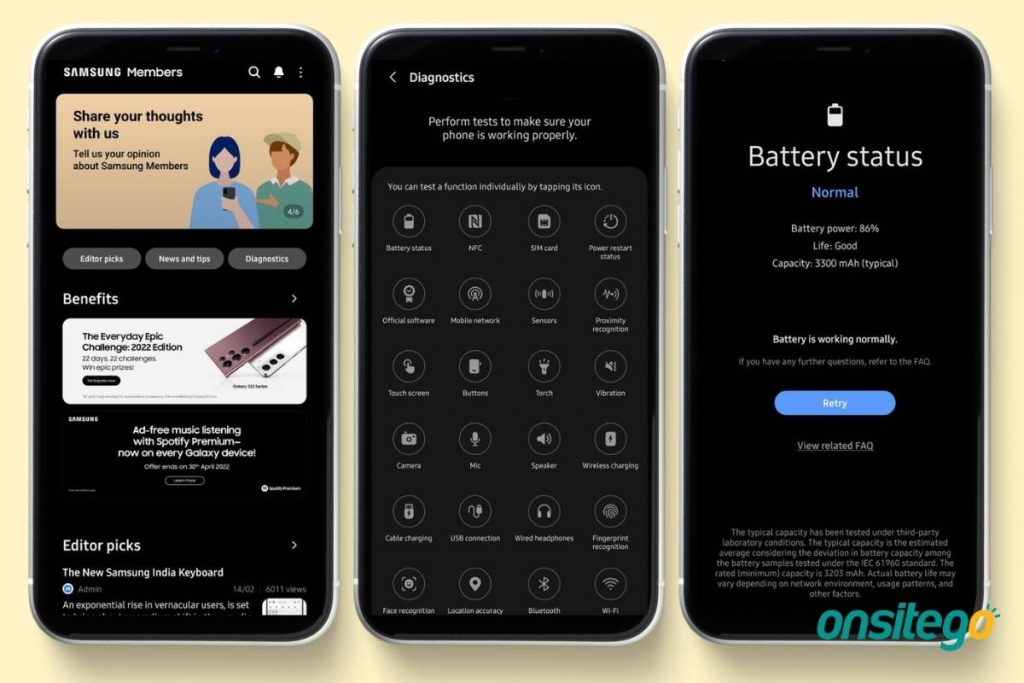
If you’re concerned that one or more of your smartphone’s functions aren’t working as they should, here’s how to use the Samsung Members app to detect and resolve problems.
- Step 1: Open the Samsung Members app on your Galaxy smartphone through the app drawer.
- Step 2: Navigate to the Diagnostics section and click on Test all, to run diagnostics. You may also tap on a specific component you’d like to test to independently check the findings.
- Step 3: Once the tests are complete, the investigation’s findings will be shown on your screen, along with any next steps that need to be taken.
The diagnostic test in the Samsung Members app covers the following 24 components:
- Battery Status: Battery status, often known as battery health, is a metric that indicates whether your battery is in good working order, or if it has deteriorated or has other issues that prohibit it from performing at its best.
- NFC: NFC (Near Field Communication) is a wireless communication protocol that is based on proximity. You may use apps like Google Pay, Samsung Pay, and others to make mobile payments. The test determines whether the functionality is working properly.
- SIM Card: If you’re not getting cellular signal from your network provider, it’s possible that your SIM cards or slots aren’t working properly. This is verified by the SIM card test.
- Power Restart Status: This section of the Samsung Members application shows you how long it has been since you’ve last restarted your phone. You may also use this page to set up automatic restarts.
- Official Software: Software is what allows hardware to function as intended by the manufacturer. It is made up of codes developed by programmers in order to create hardware devices. This test determines if you’re using the Samsung-supplied official software or a modified version such as custom ROM.
- Mobile Network: If you have a weak or no signal on your Galaxy phone, you may be unable to connect to the internet; and your ability to make or receive phone calls may be hampered. The network connection settings may be checked out during this test.
- Sensors: A sensor is a device that recognizes and records changes in the surrounding environment before sending the information to the operating system. Modern-day smartphones include a slew of sensors (accelerometer, ambient light, barometer, compass, gyro, fingerprint, and heart-rate) that aid in the device’s day-to-day operation. This test examines all the available sensors.
- Proximity Recognition: The proximity sensor detects the presence of an object when it enters its field. A very simple example is when a user holds the phone close to their face during a call, the proximity sensor detects this and switches off the display to prevent unintended keypad presses and power consumption from the display.
- Touch Screen: If a portion of your touch screen isn’t recognising your actions and you’re not sure whether the touch screen is malfunctioning, this test could be for you. This test will require you to swipe across your whole screen, looking for any locations that may have been missed.
- Buttons: At the very least, smartphones have three physical buttons: the Power, Volume Up, and Volume Down keys. The three navigation buttons or a home button may be present on certain older handsets. This test determines if one or more key pushes go unnoticed.
- Torch: The torch is one of your phone’s most useful accessories; helping users with improved lighting while taking photos and functioning as a flash light.
- Vibration: The smartphone in your pocket vibrates softly on the desk or buzzes gently. It’s such a regular occurrence that we don’t even notice it. This is accomplished through the use of a vibration motor.
- Camera: Today’s smartphones come with a plethora of camera-related features. The back and front camera sensors allow you to take pictures with your smartphone.
- Mic: On Android phones, the microphone is normally located at the bottom of the device. A microphone is used in a variety of audio recording services. It’s used while you’re on the phone with someone, sending voice notes, or using the recorder programme.
- Speaker: A loudspeaker is a miniature sound driver that is used to create sound in a mobile phone. When you play a piece of music or make a phone call, it is this component that generates the sound.
- Wireless Charging: The transfer of charge from a power outlet to your Samsung phone without the use of connecting brick and cable is known as wireless charging. If your phone supports it, it has a coil on the back, behind the back panel, that allows it to charge wirelessly.
- Cable Charging: Cable charging occurs when a user charges his smartphone with a USB cable and a power brick. Read about these five mistakes people make while charging their smartphones.
- USB Connection: A USB cable may be used to connect a smartphone to a laptop or computer. You can transfer practically any file from your smartphone to your PC or vice versa after you’ve connected.
- Wired Headphones: The 3.5mm headphone jack is a common audio connector. It is most commonly used for connecting a set of headphones to your smartphone. Try this diagnostic if you’re having problems hearing sound output on your wired headphones.
- Fingerprint Recognition: Fingerprint sensors are quite useful. You may use them to quickly and simply log into our phones, approve payments, and secure your smartphone. If you’re having difficulties with fingerprint recognition, this could be worth a try.
- Face Recognition: Facial recognition is a method of recognising or verifying a person’s identification by looking at their face. If you’re experiencing troubles unlocking your phone with Face Unlock or if it’s acting strangely, the Samsung Members app’s Face Recognition diagnostic tool can be useful.
- Location Accuracy: Apps that have been granted location permission can use your phone’s location to provide you with location-based information, services, or advertisements. Google Maps is a basic illustration of how location accuracy may be beneficial, assisting you in locating your device and guiding you along the correct pathways.
- Bluetooth: Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology standard for transmitting data over short distances. When you’re trying to connect to an external audio device and it won’t pair or transfer data, this is a typical case of it malfunctioning. You can read more about Bluetooth and its versions and features in our in-depth article.
- Wi-Fi: Wi-Fi is a wireless data transmission technology that uses radio waves to link devices such as your Samsung smartphones to the Internet. Users can connect to a Wi-Fi network to access the internet. You can read more about Wi-Fi, its features, and its various versions in our in-depth article.
My Problem Isn’t Covered Under Diagnostic Tests, What Should I Do?
If your problem isn’t addressed in the diagnostic test section and you need extra assistance, there are a few alternative options you may attempt.
1. Ask For Help In ‘Community’ Section
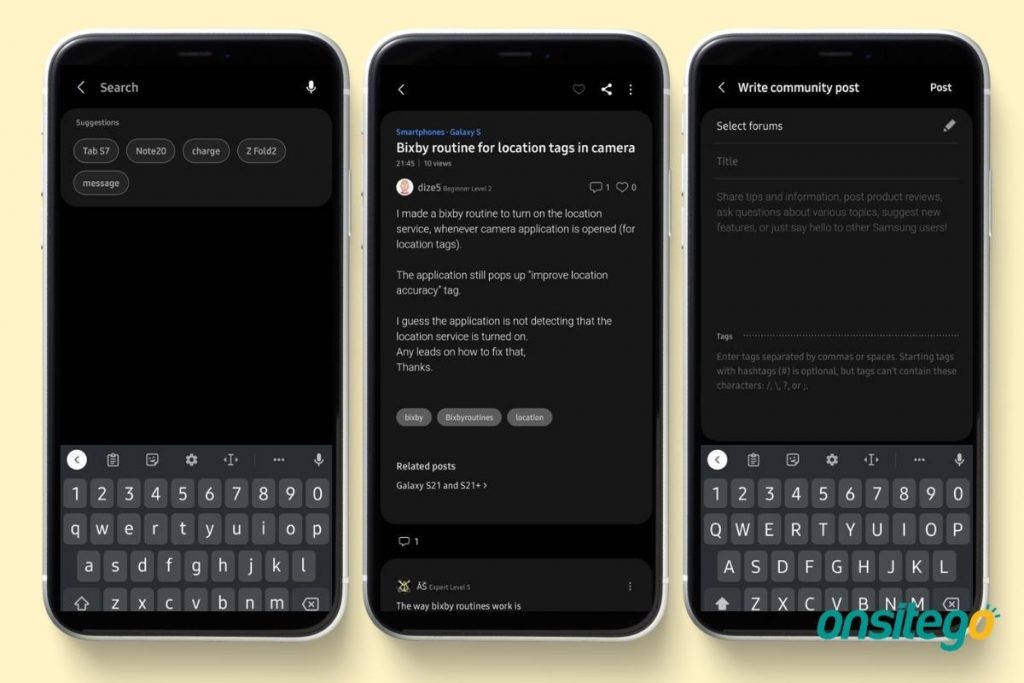
Users can also go through past Community discussion threads to see if anybody else has experienced the very same problem and if there is a solution that has previously worked. Unsatisfied users may also post a query in the Community forum and receive responses from other Samsung consumers.
- Step 1: Open the Samsung Members app and go to the Community tab.
- Step 2: You may scroll through a list of open forum posts, enlarge a thread to react, or observe the conversation by tapping on it.
- Step 3: Users may also use the Search option on the home area, which has a magnifying glass icon, to look for a certain topic.
- Step 4: To start a new thread, hit the Pencil icon, choose a category, type a title, describe your issue, and then tap Post.
2. Use ‘Get Help’ Tab
The Get Help tab is where users may find official Samsung articles with troubleshooting instructions and general information regarding Galaxy devices. As with the Community, to find a specific article relating to your problem, choose the Browse icon and start describing your concern. If no solution happens to be working, you can alternatively text, phone, or submit a service request via the application.
That said, how helpful do you find the Samsung Members app from Samsung? Do let us know by dropping a comment down below.

